Description







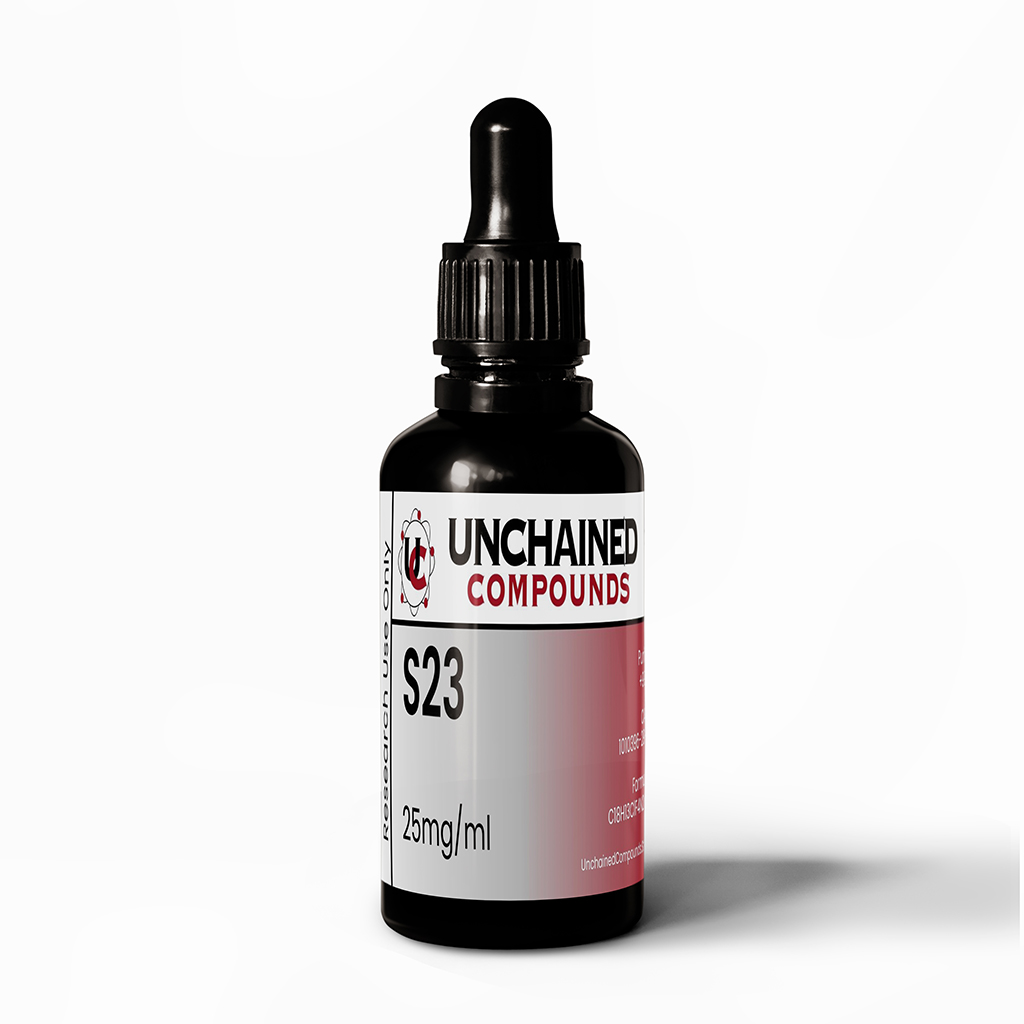
S-23 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) currently being studied and dissected for potentially treating patients with muscle wasting and osteoporosis.
Specifications
- Chemical Formula: C21H27N2O5P
- Molecular Mass: 418.42
- Synonyms: (2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[[(1R)-1-aminoethyl]-hydroxy-phosphoryl]methyl]-3-phenyl-propanoyl]amino]-3-phenyl-propanoic acid
- CAS Number: 1010396-29-8
- PubChem: 24892822
- Total Amount of the Active Ingredient: 25 mg/ml
- Shelf Life: 36 months
Research Studies
Abstract
Background: Oryza glumaepatula represents an important resource of genetic diversity that can be used to improve rice production. However, hybrid sterility severely restricts gene flow between Oryza species, and hinders the utilization of distant heterosis in hybrid rice breeding.
Results: In order to fully exploit the beneficial genes of O. glumaepatula and facilitate the conservation of these gene resources, a set of chromosome single-segment substitution lines (SSSLs) was developed using an indica variety HJX74 as the recurrent parent and an accession of O. glumaepatula as the donor parent. During the process of SSSLs development, S23, a locus conferring hybrid male sterility between O. sativa and O. glumaepatula, was identified and fine mapped to 11.54 kb and 7.08 kb genomic region in O. sativa and O. glumaepatula, respectively, encoding three and two candidate ORFs, respectively. qRT-PCR and sequence analysis excluded one common ORF as the candidate gene. In addition, hybrid male sterility caused by S23 was environment-sensitive, and could be observed only in natural short-day (NSD).
Conclusion: Identification and candidate genes analysis of S23 in this study provides a valuable example to study the crosstalk between interspecific F1 hybrid male sterility and environment-conditioned male sterility in rice, facilitates reserving and utilizing favorable genes or alleles of wild Oryza species, and allows for a more efficient exploitation of distant heterosis in hybrid rice breeding.
Abstract
Previous studies show that some ribosomal proteins possess antimicrobial peptide (AMP) activity. However, information as such remains rather fragmentary and rather limited. We showed here for the first time that amphioxus RPS23, BjRPS23, was a previously uncharacterized AMP. It not only acted as a pattern recognition receptor, capable of identifying LPS, LTA and PGN, but also an effector, capable of killing the Gram-negative and -positive bacteria. We also showed that the residues positioned at 67-84 formed the core region for the antimicrobial activity of BjRPS23, and its orthologues Verrucomicrobia RPS1268-85 and Thermotoga RPS1265-82 similarly displayed some antibacterial activities. BjRPS23 functioned by a combined action of membranolytic mechanisms including interaction with bacterial membrane via LPS, LTA and PGN, and membrane depolarization. BjRPS23 also stimulated production of intracellular ROS in bacteria. Moreover, we demonstrated that RPS23 existed across widely separated taxa, and might play a universal role in protection against bacterial infection in different animals. In addition, we found that neither BjRPS23 nor its truncated form BjRPS2367-84 were cytotoxic to mammalian cells, making them promising lead molecules for the design of novel peptide antibiotics against bacteria. Collectively, these indicate that RPS23 is a new member of AMP with ancient origin and high conservation.
Thiosulfate oxidation by Comamonas sp. S23 isolated from a sulfur spring
Abstract
A bacterial isolate S23 capable of oxidizing thiosulfate was isolated from a sulfur spring. Strain S23 is gram-negative, aerobic, and motile. The G + C content of DNA is 61.4 mol%. The fatty acid composition and phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain S23 showed that it is related to the members of the genus Comamonas, and most closely related to Comamonas testosteroni (99.9% sequence similarity). The isolate S23 exhibited thiosulfate oxidation under a mixotrophic growth condition. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using soxB-specific primers and DNA sequencing showed the presence of the soxB gene. This is the first report in Comamonas sp. showing thiosulfate oxidation under a mixotrophic growth condition.
Disclaimer
The information provided above is not intended to substitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Should you have any questions regarding a medical condition, seek the advice of your physician or a qualified healthcare provider. In no case should medical advice be disregarded or delayed because of what you have read or seen. We bear no responsibility or liability for your use of any of our research compounds and products. Please note that they are being sold for research purposes ONLY. We do NOT condone any personal use.
NOTE: In some cases wherein the assigned top colors are out of stock, a different top color will be used to ensure that your order will not be delayed. Should you need assistance identifying the peptide vial that you received, please send us an email at support@unchainedcompounds.store
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.